-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Discovery of Cells
Discovery of Cells
1665
% complete
Robert Hooke observed and described cells for the first time while examining cork under a microscope.
Image source: Cell (biology)

Cell Theory
1839
% complete
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann formulated the cell theory, stating that all living organisms are made up of cells, and cells are the basic units of life.
Image source: Cell theory

Electron Microscope
1931
% complete
Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll developed the electron microscope, enabling scientists to observe cellular structures in greater detail.
Image source: Electron microscope

Cell Division and Reproduction
Mitosis
1873
% complete
Walther Flemming discovered and described the process of mitosis, which is the division of a cell into two identical daughter cells.
Image source: Mitosis
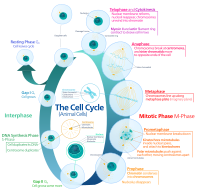
Meiosis
1883
% complete
Edouard Van Beneden discovered and described meiosis, a specialized type of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
Image source: Meiosis

Cell Structure and Function
Nucleus Discovery
1884
% complete
Albrecht Kossel identified and named the nucleus, a distinct structure within cells that contains genetic material.
Chromosomes
1888
% complete
Walther Flemming discovered and named chromosomes, the thread-like structures that carry genetic information.
Image source: Chromosome

DNA Structure
1953
% complete
James Watson and Francis Crick proposed the double helix structure of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information.
Image source: DNA

Cell Membrane Model
1972
% complete
Singer and Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane, describing it as a dynamic structure composed of lipids and proteins.
Image source: Fluid mosaic model

Modern Cell Biology
Cell Culture
1955
% complete
Theodore Puck and Philip Marcus developed techniques for growing cells outside the body, leading to advancements in medical research and biotechnology.
Image source: Cell culture

Stem Cell Discovery
1981
% complete
Gail Martin and Martin Evans independently discovered and isolated embryonic stem cells, which have the potential to develop into various cell types.
Image source: Stem cell
Human Genome Project
1990 - 2003
% complete
The Human Genome Project was initiated to sequence and map the entire human genome, providing crucial insights into genetic information and its role in health and disease.
Image source: Human Genome Project

CRISPR-Cas9
2012
% complete
Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier developed the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool, revolutionizing genetic research and potential applications in medicine.
Image source: CRISPR

Key Facts
- 1665: Robert Hooke observes cells in cork under a microscope.
- 1838: Matthias Schleiden proposes that plants are composed of cells.
- 1839: Theodor Schwann proposes that animals are composed of cells.
- 1855: Rudolf Virchow introduces the concept of cell division.
- 1953: James Watson and Francis Crick discover the structure of DNA.
Source
This Cell History timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].