-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Roman Empire Timeline
(753 BC - 476 AD)Political and Social Developments
Founding of the Roman Republic
509 BC
% complete
The Roman Republic was established after the overthrow of the last Roman king, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. This marked the beginning of the republican era in Rome, characterized by a system of government with elected officials and a Senate.
Image source: Roman Republic

Julius Caesar's Assassination
Mar 15, 44 BC
% complete
Julius Caesar, a prominent Roman general and statesman, was assassinated by a group of senators led by Brutus. This event resulted in a power struggle and ultimately led to the end of the Roman Republic.
Image source: Assassination of Julius Caesar

Construction of the Colosseum
70 AD
% complete
The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre, was completed during the reign of Emperor Vespasian. This iconic structure became a symbol of Roman engineering and hosted various spectacles, including gladiatorial contests and public events.
Image source: Colosseum

Construction of the Pantheon
118 AD - 125 AD
% complete
The Pantheon, a temple dedicated to all the gods of ancient Rome, was built during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. It is renowned for its architectural grandeur and remains one of Rome's most iconic landmarks.
Image source: Pantheon, Rome

Construction of Hadrian's Wall
122 AD
% complete
Emperor Hadrian ordered the construction of Hadrian's Wall, a defensive fortification in northern Britain. This wall marked the northern limit of the Roman Empire and served as a symbol of Roman power and control.
Image source: Hadrian's Wall

Antonine Plague
165 AD - 180 AD
% complete
The Antonine Plague, also known as the Plague of Galen, was an ancient pandemic that swept through the Roman Empire, causing widespread death and economic disruption.
Image source: Antonine Plague

Construction of the Roman Baths of Caracalla
212 AD - 216 AD
% complete
Emperor Caracalla initiated the construction of the Roman Baths of Caracalla, one of the largest and most luxurious thermal baths in ancient Rome. It served as a social gathering place and showcased Roman engineering prowess.
Image source: Caracalla

Battle of Milvian Bridge
Oct 28, 312 AD
% complete
The Battle of Milvian Bridge was a pivotal moment in the rise of Christianity. Emperor Constantine claimed to have seen a vision of a Christian symbol before the battle and emerged victorious. This event contributed to the eventual adoption of Christianity as the state religion.
Image source: Battle of the Milvian Bridge

Edict of Milan
313 AD
% complete
The Edict of Milan, issued by Emperor Constantine, granted religious tolerance to Christians within the Roman Empire. This edict marked a significant shift in Roman policy towards Christianity and paved the way for its eventual adoption as the state religion.
Image source: Edict of Milan

Expansion and Conquest
Battle of Cannae
Aug 2, 216 BC
% complete
The Battle of Cannae was a major military encounter during the Second Punic War between Rome and Carthage. Carthaginian general Hannibal achieved a decisive victory by employing a double-envelopment tactic, resulting in heavy Roman casualties.
Image source: Battle of Cannae

Battle of Zama
Oct 19, 202 BC
% complete
The Battle of Zama was a decisive victory for Rome over Carthage during the Second Punic War. Roman general Scipio Africanus defeated Carthaginian leader Hannibal, effectively ending Carthage's threat to Rome.
Image source: Battle of Zama
Battle of Actium
Sep 2, 31 BC
% complete
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle between the forces of Octavian (later known as Augustus) and Mark Antony and Cleopatra. Octavian's victory secured his position as the sole ruler of Rome and marked the end of the Roman Republic.
Image source: Battle of Actium

Battle of Teutoburg Forest
Sep, 9 AD
% complete
The Battle of Teutoburg Forest was a devastating defeat for the Roman Empire at the hands of Germanic tribes led by Arminius. This defeat halted Roman expansion into Germania.
Image source: Battle of the Teutoburg Forest

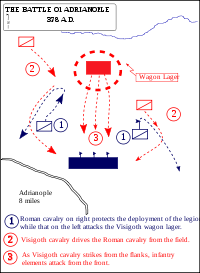
Battle of Adrianople
Aug 9, 378 AD
% complete
The Battle of Adrianople, fought between the Roman Empire and the Visigoths, resulted in a decisive victory for the Visigoths and marked a significant turning point in Roman military history. It was the first time a Roman emperor, Valens, was killed in battle.
Image source: Battle of Adrianople
Emperors
Reign of Augustus
27 BC - 14 AD
% complete
Augustus, the first Roman emperor, ruled for over four decades, initiating the Pax Romana and implementing significant political and social reforms that shaped the empire's future.
Image source: Augustus

Reign of Marcus Aurelius
161 AD - 180 AD
% complete
Marcus Aurelius, known for his philosophical writings, ruled during a challenging period marked by military conflicts and the Antonine Plague. His reign is often associated with the decline of the Roman Empire.
Image source: Marcus Aurelius

Decline and Fall
Fall of the Western Roman Empire
Sep 4, 476 AD
% complete
The Fall of the Western Roman Empire marked the end of ancient Rome. The last Roman emperor, Romulus Augustus, was deposed by Odoacer, a Germanic chieftain, leading to the dissolution of the Western Roman Empire.
Image source: Fall of the Western Roman Empire
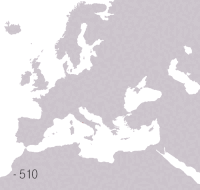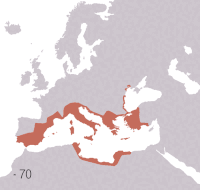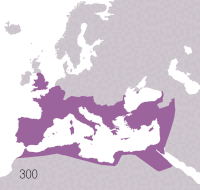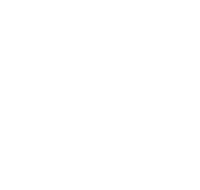
Key Facts
- The Roman Republic was established in 509 BC after the overthrow of the Etruscan monarchy.
- Julius Caesar rose to power as a military leader and declared himself dictator of Rome in 45 BC.
- Under Augustus, the first emperor, the Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent in 117 AD.
- The Pax Romana, a period of relative peace and stability, lasted from 27 BC to 180 AD.
- The fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD marked the end of ancient Rome and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
Source
This Roman Empire timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].