-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Preparations
Kennedy's Moon Speech
May 25, 1961
% complete
On May 25, 1961, John F. Kennedy delivered a speech to a joint session of Congress, where he famously stated that the United States should set a goal of landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to Earth before the end of the decade. This speech, known as Kennedy's Moon Speech, set in motion the Apollo program and the race to the Moon.
Image source: We choose to go to the Moon

Apollo Program Initiated
Jul 20, 1961
% complete
Apollo Program Initiated was a spaceflight program by NASA that ran from 1961 to 1972. It was designed to land astronauts on the Moon and return them safely to Earth. The program was announced by President John F. Kennedy on May 25, 1961, and its goal was accomplished with the Apollo 11 mission on July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to set foot on the Moon.
Image source: Apollo 11

Apollo 1 Fire
Jan 27, 1967
% complete
Apollo 1 Fire: On January 27, 1967, tragedy struck during a pre-launch test for Apollo 1, resulting in the deaths of astronauts Gus Grissom, Edward H. White, and Roger B. Chaffee. A flash fire broke out in the command module, suffocating the crew within seconds. This devastating event highlighted the risks and challenges of space exploration, leading to significant safety improvements in subsequent missions.
Image source: Apollo 1

Apollo 7 Mission
Oct 11, 1968 - Oct 22, 1968
% complete
Apollo 7 Mission was the first manned mission in the Apollo program that launched on October 11, 1968, and returned on October 22, 1968. The mission's objectives were to test the Apollo command module in Earth orbit, evaluate the performance of the crew and the spacecraft systems, and demonstrate the ability to carry out the rendezvous and docking maneuvers with the lunar module. The mission achieved all of its objectives and paved the way for future manned missions to the Moon.
Image source: Apollo 7

Apollo 8 Lunar Orbit
Dec 24, 1968 - Dec 25, 1968
% complete
Apollo 8 Lunar Orbit was a mission conducted by NASA's Apollo program. It was the first crewed spacecraft to orbit the Moon. The mission lasted from December 24, 1968, to December 25, 1968. The three crew members—Commander Frank Borman, Command Module Pilot James Lovell, and Lunar Module Pilot William Anders—were the first humans to witness an Earthrise and to orbit another celestial body. This mission laid the groundwork for the subsequent Apollo missions that would lead to the Moon landing in 1969.
Image source: Lunar orbit

Apollo 9 Mission
Mar 3, 1969 - Mar 13, 1969
% complete
Apollo 9 was the third manned mission in NASA's Apollo space program and the first flight of the Command/Service Module (CSM) with the Lunar Module (LM). The mission was launched on March 3, 1969, and lasted until March 13, 1969. The primary goal of Apollo 9 was to test the complete Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit, including the lunar module. The crew performed several critical maneuvers and tests, such as docking and undocking the lunar module from the command module and conducting spacewalks to test the astronauts' ability to work outside the spacecraft.
Image source: Apollo 9

Apollo 10 Lunar Orbit
May 18, 1969 - May 26, 1969
% complete
Apollo 10 Lunar Orbit was a manned mission to orbit the Moon and serve as a dress rehearsal for the Apollo 11 mission. It took place from May 18, 1969 to May 26, 1969. The crew consisted of Commander Thomas P. Stafford, Command Module Pilot John W. Young, and Lunar Module Pilot Eugene Cernan. During the mission, the crew tested the lunar module's descent and ascent engines, performed lunar orbit rendezvous techniques, and took detailed photographs of potential landing sites for future missions. The mission was successful and paved the way for the historic Apollo 11 Moon landing in July 1969.
Image source: Apollo 10

Return and Legacy
Apollo Missions Continued
1969 - 1972
% complete
Apollo Missions Continued refers to the series of manned space missions that followed the successful Apollo 11 mission in 1969. These missions were aimed at exploring the lunar surface and conducting scientific experiments. The Apollo Missions Continued from 1969 to 1972 included Apollo 12, Apollo 14, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17.
Image source: Apollo program

Space Race Impact
1969 - 1972
% complete
The Space Race Impact refers to the period from 1969 to 1972 when the moon landing and subsequent missions had a significant impact on the United States and the Soviet Union. The successful moon landing by Apollo 11 in 1969 was a major milestone in the Space Race and demonstrated American dominance in space exploration. It also had political and social implications, boosting the morale of the American public and solidifying the United States as a global leader in science and technology. The Space Race Impact continued with subsequent Apollo missions and lunar landings, further advancing scientific knowledge and technological capabilities. The United States' successful moon missions during this period also marked the end of the Space Race, as the Soviet Union was unable to match these achievements. Overall, the Space Race Impact had a profound effect on the world by showcasing the capabilities of human space exploration and inspiring future generations of scientists and astronauts.
Image source: Space Race

Global Celebrations
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
Global Celebrations marked the day when humans first set foot on the Moon. It was a historic event that was celebrated all around the world. People gathered in public spaces to watch the live television broadcast of the Apollo 11 mission. There were fireworks, parades, and parties to commemorate this incredible achievement. It was a moment of unity and pride for humanity.
Apollo 11 Splashdown
Jul 24, 1969
% complete
Apollo 11 Splashdown was the final phase of the Apollo 11 mission, where the command module Columbia successfully returned to Earth. It occurred on July 24, 1969, in the North Pacific Ocean, near Hawaii. The mission marked the first time that humans had set foot on the moon and safely returned to Earth.
Quarantine of Astronauts
Jul 24, 1969
% complete
After returning to Earth from the Apollo 11 mission, the three astronauts, Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins, were placed in quarantine to prevent the spread of any potential lunar pathogens. They spent a total of 21 days in quarantine, first aboard the recovery ship, USS Hornet, and then in a special quarantine facility at the Johnson Space Center.
Image source: Mobile quarantine facility

Moon Rocks Returned
Jul 24, 1969
% complete
Apollo 11 returns to Earth with samples of lunar rocks, the first time samples from another celestial body have been brought back to Earth.
Image source: Moon rock

Apollo 17: Last Moon Landing
Dec 7, 1972 - Dec 19, 1972
% complete
Apollo 17 was the final mission of NASA's Apollo program and was the last mission for humans to explore the Moon. The mission launched on December 7, 1972, and landed on the Moon on December 11, 1972. The crew, consisting of Commander Eugene Cernan, Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt, and Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans, spent a total of 3 days on the lunar surface, conducting experiments, collecting samples, and performing geological surveys. The mission successfully returned to Earth on December 19, 1972, marking the end of an era in lunar exploration.
Image source: Third-party evidence for Apollo Moon landings

Apollo Program Concludes
Dec 19, 1972
% complete
The Apollo Program Concludes on December 19, 1972. After four years of manned lunar exploration, Apollo 17 becomes the final mission in the program. The crew, consisting of Eugene Cernan, Ronald Evans, and Harrison Schmitt, spend a total of 75 hours on the lunar surface during their mission. They collect valuable data and rock samples, and leave behind experiments to study the moon's environment. Upon their return to Earth, the Apollo program is officially concluded, marking the end of an era in space exploration.
Launch
Apollo 11 Launch
Jul 16, 1969
% complete
Apollo 11 Launch was the mission that successfully landed the first humans on the Moon. It took place on July 16, 1969, with astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins aboard the spacecraft. The Saturn V rocket launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and after a four-day journey, the lunar module named Eagle landed in the Sea of Tranquility on July 20. This historic event marked a major achievement for the United States in the Space Race and set the stage for future space exploration.
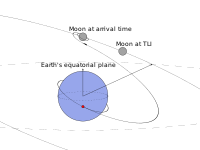
Translunar Injection
Jul 16, 1969
% complete
Translunar Injection was a maneuver performed by the Apollo spacecraft to leave Earth's orbit and begin its journey to the Moon. It took place on July 16, 1969, during the Apollo 11 mission. The command module, with astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins on board, fired the Service Module's engine to accelerate and break free from Earth's gravitational pull. This crucial maneuver allowed the spacecraft to enter a trajectory towards the Moon and start the lunar landing mission.
Image source: Trans-lunar injection
Lunar Landing
Lunar Module Separation
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
The Lunar Module (LM) separated from the Command Module (CM) in lunar orbit. This allowed the LM to descend to the surface of the moon while the CM remained in orbit. The separation occurred on July 20, 1969, during the Apollo 11 mission.
Image source: Apollo Lunar Module

Lunar Module Descent
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
The Lunar Module Descent was a crucial phase of the Apollo missions to the Moon. It involved the separation of the Lunar Module from the Command Module, as well as the descent and landing of the Lunar Module on the lunar surface. On July 20, 1969, during the Apollo 11 mission, the Lunar Module named 'Eagle' safely touched down on the Moon's surface in the region known as the Sea of Tranquility. This historic event marked the first time humans had ever landed on another celestial body.
The Eagle Has Landed
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
The Eagle Has Landed was the phrase used to signal the successful landing of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module Eagle on the Moon on July 20, 1969. The phrase was said by astronaut Neil Armstrong to Mission Control to signify that the spacecraft had safely touched down on the lunar surface. This historic moment marked the first time humans had ever set foot on another celestial body.
Moonwalk
First Moonwalk (Neil Armstrong)
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
Neil Armstrong became the first person to set foot on the moon during the Apollo 11 mission on July 20, 1969. He famously said, 'That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.' This historic event marked a significant milestone in space exploration and the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Image source: Neil Armstrong

One small step for man...
Jul 20, 1969
% complete
One small step for man... (Jul 20, 1969)
Lunar Module Ascent
Jul 21, 1969
% complete
The Lunar Module Ascent was a crucial part of the Apollo Moon landing mission. On July 21, 1969, the Lunar Module (LM) known as Eagle, which had landed on the Moon's surface, launched from the Moon to rendezvous with the Command Module in lunar orbit. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin piloted the LM ascent stage to return to the Command Module and reunite with astronaut Michael Collins. The successful ascent marked an important milestone in the mission, as it allowed the astronauts to safely leave the lunar surface and begin their journey back to Earth.
Lunar Module Docking
Jul 21, 1969
% complete
The Lunar Module, named Eagle, successfully docks with the Command Module, named Columbia, in lunar orbit. This critical maneuver ensures that the astronauts can return to Earth safely after their mission on the moon. The docking took place on July 21, 1969, during the Apollo 11 mission.
Key Facts
- Apollo 11 was the first mission to land humans on the moon.
- Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the moon on July 20, 1969.
- Buzz Aldrin joined Armstrong on the moon, while Michael Collins orbited above in the command module.
- The moon landing was a major achievement for the United States in the Space Race against the Soviet Union.
- The Apollo 11 mission successfully returned to Earth on July 24, 1969.
Source
This Moon Landing timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].