-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Major Battles and Campaigns
Battle of Fort Sumter
Apr 12, 1861
% complete
The Battle of Fort Sumter was the first military engagement of the American Civil War. It took place on April 12-13, 1861, when Confederate forces fired upon the Union garrison at Fort Sumter in South Carolina.
Image source: Battle of Fort Sumter

Battle of Fort Sumter ends
Apr 14, 1861
% complete
The Battle of Fort Sumter was the first battle of the Civil War. It began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces attacked Fort Sumter, a Union stronghold in Charleston, South Carolina. The battle lasted for 34 hours and ended on April 14, 1861, when the Union forces surrendered. This event marked the beginning of the Civil War.
First Battle of Bull Run
Jul 21, 1861
% complete
The First Battle of Bull Run, also known as the First Battle of Manassas, was fought on July 21, 1861. It was the first major battle of the American Civil War. The Confederate forces, commanded by General P.G.T. Beauregard, defeated the Union forces, commanded by General Irvin McDowell, near Manassas, Virginia. The battle ended in a Confederate victory and demonstrated that the war would not be easily won by either side.
Battle of First Bull Run ends
Jul 21, 1861
% complete
The Battle of First Bull Run ends on July 21, 1861. It was the first major battle of the American Civil War and resulted in a Confederate victory. The battle took place near Manassas, Virginia and involved around 35,000 Union troops and 20,000 Confederate troops. The Union army, commanded by Brigadier General Irvin McDowell, launched an offensive against the Confederate forces, led by General P.G.T. Beauregard. Despite initially gaining ground, the Union forces were eventually repelled by Confederate reinforcements led by General Thomas J. Jackson, earning him the nickname 'Stonewall.' The Confederate victory at the Battle of First Bull Run boosted morale and confidence in the South, while highlighting the challenges that the Union would face in the war.
Image source: First Battle of Bull Run

Battle of Pea Ridge
Mar 6, 1862 - Mar 8, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Pea Ridge, also known as the Battle of Elkhorn Tavern, was fought from March 6 to March 8, 1862, in northwestern Arkansas during the American Civil War. It was the largest battle fought west of the Mississippi River and resulted in a Union victory. The battle was significant because it secured Missouri for the Union and helped prevent Confederate forces from gaining control of the Mississippi River.
Image source: Battle of Pea Ridge

Battle of Glorieta Pass
Mar 26, 1862 - Mar 28, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Glorieta Pass, often referred to as the Gettysburg of the West, was fought from March 26 to March 28, 1862, in the New Mexico Territory. Union forces clashed with Confederate troops in an attempt to control the strategic pass and disrupt Confederate supply lines. Although the battle was inconclusive, the Union victory prevented the Confederates from gaining control of the Southwest and effectively ended their invasion of New Mexico.
Image source: Battle of Glorieta Pass

Battle of Shiloh
Apr 6, 1862 - Apr 7, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. It was fought on April 6 and 7, 1862, in southwestern Tennessee. The Union Army, under Major General Ulysses S. Grant, was attacked by the Confederate Army, commanded by General Albert Sidney Johnston and General P.G.T. Beauregard. The battle resulted in a Union victory but at a high cost in casualties. It was one of the bloodiest battles of the war, with over 23,000 total casualties.
Image source: Battle of Shiloh

Battle of Glendale
Jun 30, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Glendale, also known as the Battle of Frayser's Farm, was fought on June 30, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, during the American Civil War. It was the fifth of the Seven Days Battles (June 25 – July 1) of the Peninsula Campaign, and took place just 8 miles east of the Confederate capital of Richmond. The battle resulted in a Confederate victory, but it was a strategic opportunity squandered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee.
Image source: Battle of Glendale

Battle of Malvern Hill
Jul 1, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Malvern Hill was fought on July 1, 1862, during the American Civil War. It was the final battle of the Seven Days' Battles in the Peninsula Campaign, and it took place in Henrico County, Virginia. The Confederate Army, led by General Robert E. Lee, launched a series of attacks against the Union Army's defensive positions on Malvern Hill. Despite heavy casualties, the Union Army held their ground and successfully repelled the Confederate attacks. The battle was a tactical victory for the Union and marked the end of the Peninsula Campaign.
Image source: Battle of Malvern Hill

Battle of South Mountain
Sep 14, 1862
% complete
The Battle of South Mountain took place on September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate forces under General Robert E. Lee attempted to open a northern front in Maryland by crossing the Potomac River and invading Union territory. Union forces, led by Major General George B. McClellan, intercepted Lee's army at South Mountain, resulting in a series of skirmishes and battles that lasted throughout the day. Despite being outnumbered, the Union forces were able to hold their ground and repel the Confederate attacks. The Battle of South Mountain is considered a significant turning point in the Civil War, as it delayed Lee's invasion plans and allowed McClellan to gather intelligence and reinforcements for the impending Battle of Antietam.
Image source: Battle of South Mountain

Battle of Antietam
Sep 17, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Antietam, also known as the Battle of Sharpsburg, was fought on September 17, 1862, during the American Civil War. It was the first major battle fought on Northern soil and was one of the bloodiest battles of the war. The Union Army, led by General George McClellan, faced off against the Confederate Army, commanded by General Robert E. Lee. The battle ended in a tactical draw, but it was a strategic victory for the Union as it halted Lee's invasion of the North and provided a much-needed boost to Union morale.
Image source: Battle of Antietam

Battle of Shepherdstown
Sep 19, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Shepherdstown, also known as the Battle of Boteler's Ford, was fought on September 19 and 20, 1862, in Jefferson County, Virginia (now West Virginia), during the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the final battle of the campaign, and resulted in a tactical Confederate victory. The battle was mainly skirmishing and artillery fire, with little infantry involvement. Despite the Confederate victory, the battle did not affect the strategic outcome of the Maryland Campaign.
Image source: Battle of Shepherdstown

Battle of Fredericksburg
Dec 11, 1862 - Dec 15, 1862
% complete
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought from December 11 to December 15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, during the American Civil War. The Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by General Robert E. Lee, successfully defended the town against the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Major General Ambrose E. Burnside. The battle resulted in a decisive Confederate victory.
Image source: Battle of Fredericksburg

Battle of Chancellorsville
Apr 30, 1863 - May 6, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Chancellorsville was a major battle during the American Civil War. It took place from April 30 to May 6, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia. The battle was fought between the Army of the Potomac, commanded by General Joseph Hooker, and the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by General Robert E. Lee. Despite having superior numbers, Hooker's attack was repulsed by Lee, who executed a daring flanking maneuver that forced the Union army to retreat. The battle is notable for the death of Confederate General Stonewall Jackson, who was accidentally shot by his own men and died several days later. The Confederate victory at Chancellorsville boosted their morale and confidence, but it came at a high cost with heavy casualties on both sides.
Image source: Battle of Chancellorsville

Battle of Raymond
May 12, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Raymond was fought on May 12, 1863, during the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. It was part of a series of engagements that took place in western Mississippi, where Union forces under General Ulysses S. Grant were trying to capture the city of Vicksburg. The battle resulted in a Union victory and played a significant role in Grant's successful campaign to take control of the Mississippi River.
Image source: Battle of Raymond

Battle of Champion Hill
May 16, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Champion Hill, also known as the Battle of Bakers Creek, was fought on May 16, 1863, during the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. The Union Army, commanded by Major General Ulysses S. Grant, sought to capture the Confederate stronghold of Vicksburg, Mississippi. The Confederate Army, commanded by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, tried to prevent the Union forces from reaching Vicksburg. The battle ended with a Union victory, and it marked a turning point in the Vicksburg Campaign.
Siege of Vicksburg
May 18, 1863 - Jul 4, 1863
% complete
The siege of Vicksburg took place from May 18, 1863, to July 4, 1863, during the American Civil War. The Union Army, under the command of General Ulysses S. Grant, laid siege to the Confederate stronghold of Vicksburg, Mississippi. The siege lasted for 47 days, and the Confederate forces eventually surrendered on July 4, 1863. This victory for the Union was a turning point in the war, as it gave them control of the Mississippi River and split the Confederacy in half.
Image source: Siege of Vicksburg

Battle of Gettysburg
Jul 1, 1863 - Jul 3, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Gettysburg was fought from July 1 to July 3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Considered one of the most important engagements of the American Civil War, it was the largest battle ever fought in North America. The Union Army, commanded by General George G. Meade, defeated General Robert E. Lee's Confederate Army, effectively ending Lee's second invasion of the North. The battle resulted in heavy casualties on both sides, with over 50,000 soldiers killed, wounded, or missing.
Image source: Battle of Gettysburg

Battle of Gettysburg ends
Jul 3, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Gettysburg ends on July 3, 1863. It was a major turning point in the Civil War, with the Union Army of the Potomac successfully defending against the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia. The battle resulted in high casualties on both sides, but it marked a significant victory for the Union and boosted their morale. The Confederate Army was forced to retreat, and this defeat was a major setback for their efforts to invade the North.
Battle of Fort Wagner
Jul 11, 1863 - Sep 7, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Fort Wagner took place from July 11, 1863, to September 7, 1863, during the American Civil War. It was fought on Morris Island in Charleston Harbor, South Carolina, between the Union Army and the Confederate Army. The Union Army attempted to capture Fort Wagner, a key fortification guarding the entrance to Charleston Harbor. The Confederate Army, under the command of General P.G.T. Beauregard, defended the fort and launched several counterattacks. The battle resulted in heavy casualties for both sides, with the Union Army suffering particularly high losses. Despite their efforts, the Union forces were unable to capture Fort Wagner, and the fort remained under Confederate control until September 7, 1863.
Image source: Second Battle of Fort Wagner

Battle of Chickamauga
Sep 19, 1863 - Sep 20, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Chickamauga was fought between the Union Army of the Cumberland and the Confederate Army of Tennessee on September 19-20, 1863, during the American Civil War. It was one of the bloodiest battles of the war and marked a significant Confederate victory. The battle took place in northwestern Georgia, near the town of Chickamauga, and was part of the larger Chickamauga Campaign. The Confederate forces, led by General Braxton Bragg, successfully defeated the Union forces, commanded by General William Rosecrans, and forced them to retreat to Chattanooga. The battle resulted in high casualties for both sides, with over 34,000 total casualties. Despite the Confederate victory, they were unable to fully capitalize on their success and capture Chattanooga, which remained a strategic stronghold for the Union. The Battle of Chickamauga is considered a turning point in the Civil War as it allowed the Confederates to regain control of Chattanooga and set the stage for the subsequent battles in the Chattanooga Campaign.
Image source: Battle of Chickamauga

Battle of Chickamauga ends
Sep 20, 1863
% complete
The Battle of Chickamauga ends on September 20, 1863. It was one of the largest and bloodiest battles of the American Civil War, fought between the Confederate Army of Tennessee commanded by General Braxton Bragg and the Union Army of the Cumberland commanded by General William Rosecrans. The battle resulted in a Confederate victory and forced the Union army to retreat back to Chattanooga, Tennessee.
Battle of Olustee
Feb 20, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Olustee was fought on February 20, 1864, in Florida during the American Civil War. It was the largest battle fought in Florida during the war, and resulted in a Confederate victory.
Image source: Battle of Olustee

Battle of Fort Pillow
Apr 12, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Fort Pillow took place on April 12, 1864, during the American Civil War. It was a Confederate victory in which Confederate soldiers under the command of General Nathan Bedford Forrest attacked Union troops garrisoned at Fort Pillow, a fortification on the Mississippi River in Henning, Tennessee. The Union troops, consisting mainly of African-American soldiers, were heavily outnumbered and poorly equipped. During the battle, the Confederate forces overran the fort and killed many of the Union soldiers, including a large number of African-Americans. The battle gained notoriety due to the high number of casualties and the brutal treatment of Union prisoners and African-American soldiers by Confederate troops.
Battle of Fort Pillow ends
Apr 12, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Fort Pillow ends on April 12, 1864. It was a battle fought between the Confederate Army and Union forces during the American Civil War. The battle took place at Fort Pillow in Tennessee and resulted in a Confederate victory. The Confederate forces, led by General Nathan Bedford Forrest, attacked the fort and overwhelmed the Union garrison. The battle is particularly notable for the high number of casualties among the Union forces, as well as allegations of war crimes committed against African American soldiers by the Confederate troops.
Image source: Battle of Fort Pillow

Atlanta Campaign
May 7, 1864 - Sep 2, 1864
% complete
The Atlanta Campaign was a series of military battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. It began on May 7, 1864, and lasted until September 2, 1864. The campaign was led by Union General William Tecumseh Sherman against Confederate General Joseph E. Johnston and eventually resulted in the capture of Atlanta by Union forces.
Image source: Atlanta campaign

Battle of Spotsylvania Court House
May 8, 1864 - May 21, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Spotsylvania Court House was a significant battle that took place during the American Civil War. It lasted from May 8 to May 21, 1864. The battle was fought in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, between the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant, and the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by General Robert E. Lee. The battle resulted in heavy casualties on both sides and ended inconclusively, with neither army gaining a decisive victory.
Battle of Spotsylvania Court House ends
May 21, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Spotsylvania Court House was a significant battle that took place during the American Civil War. It was fought from May 8 to May 21, 1864, as part of Union General Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia. The battle resulted in heavy casualties on both sides and is known for its intense and prolonged fighting, particularly in the area known as the Bloody Angle. After two weeks of intense combat, the battle ended inconclusively, with both sides suffering heavy losses but no significant territorial gains. Despite the lack of a clear victory, the battle marked a turning point in the war, as Grant continued to press forward and kept Lee on the defensive.
Image source: Battle of Spotsylvania Court House

Battle of Cold Harbor
May 31, 1864 - Jun 12, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Cold Harbor was a series of battles and skirmishes fought in Virginia during the American Civil War. It took place from May 31 to June 12, 1864. The Union Army, led by General Ulysses S. Grant, launched multiple attacks on Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia in an attempt to seize control of the vital crossroads at Cold Harbor. However, the Confederate forces were able to hold their positions and repel the Union assaults, resulting in heavy casualties for both sides. The Battle of Cold Harbor is often remembered as one of the bloodiest and most pointless battles of the Civil War.
Battle of Cold Harbor ends
Jun 12, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Cold Harbor ends on June 12, 1864. It was fought during the American Civil War near Mechanicsville, Virginia. It was one of the final battles in the Overland Campaign and resulted in a Confederate victory. The battle is known for its high casualties and the failed Union assault on Confederate trenches.
Image source: Battle of Cold Harbor

Battle of Petersburg
Jun 15, 1864 - Apr 2, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Petersburg was a series of battles fought in and around Petersburg, Virginia, from June 15, 1864, to April 2, 1865, during the American Civil War. The Union Army, led by General Ulysses S. Grant, sought to capture Petersburg, a key supply center for the Confederate Army. The Confederate Army, led by General Robert E. Lee, defended Petersburg in a series of trench warfare battles. The Battle of Petersburg resulted in a Union victory and marked a turning point in the war as it weakened the Confederate Army's defenses and set the stage for its eventual surrender.
Image source: Siege of Petersburg

Atlanta Campaign ends
Sep 2, 1864
% complete
The Atlanta Campaign was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, culminating in the Union capture of Atlanta, Georgia. It lasted from May 1 to September 2, 1864.
Sherman's March to the Sea
Nov 15, 1864 - Dec 21, 1864
% complete
Sherman's March to the Sea was a military campaign led by General William Tecumseh Sherman during the American Civil War. It took place from November 15 to December 21, 1864, and involved Sherman's Union Army forces marching from Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia, with the goal of devastating the Confederate's ability to wage war and to break the will of the Southern population.
Battle of Nashville
Dec 15, 1864 - Dec 16, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Nashville was a two-day battle in the American Civil War that took place on December 15–16, 1864, in Nashville, Tennessee. It was the final major battle of the war in the Western Theater, and effectively ended Confederate efforts to regain control of the region.
Image source: Battle of Nashville

Battle of Nashville ends
Dec 16, 1864
% complete
The Battle of Nashville ends on December 16, 1864. It was the last major battle of the American Civil War, fought between the Confederate Army of Tennessee and the Union Army of the Cumberland. The Union forces, under the command of Major General George H. Thomas, decisively defeated the Confederates, effectively ending their threat in the Western Theater.
Sherman's March to the Sea ends
Dec 21, 1864
% complete
Sherman's March to the Sea was a military campaign led by Union General William Tecumseh Sherman in the American Civil War from November 15 to December 21, 1864. The campaign began with Sherman's troops leaving Atlanta and marching across Georgia to reach the port city of Savannah. Along the way, they destroyed railroads, industries, and infrastructure to deprive the Confederacy of resources. The march ended when Sherman's troops reached Savannah and captured the city. The campaign was notable for its scorched earth tactics and the psychological impact it had on the Confederate states.
Image source: Sherman's March to the Sea

Battle of Bentonville
Mar 19, 1865 - Mar 21, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Bentonville was fought from March 19 to March 21, 1865, in Bentonville, North Carolina, during the American Civil War. It was the last major battle between the Union Army of the West, commanded by Major General William T. Sherman, and the Confederate Army of Tennessee, commanded by General Joseph E. Johnston. The battle resulted in a Union victory and marked the near end of the Civil War.
Battle of Bentonville ends
Mar 21, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Bentonville ends on March 21, 1865. It was the last major Confederate offensive of the American Civil War. Union forces, under the command of Major General William T. Sherman, successfully repelled the Confederate attack led by General Joseph E. Johnston. The battle resulted in a Union victory and marked a turning point in the Civil War, leading to the eventual surrender of the Confederacy.
Image source: Battle of Bentonville

Battle of Five Forks
Apr 1, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Five Forks was fought on April 1, 1865, during the American Civil War. It was a Union victory and marked the beginning of the end for the Confederate Army. General Ulysses S. Grant led the Union forces, while General Robert E. Lee commanded the Confederate troops. The battle took place in Dinwiddie County, Virginia, and resulted in a decisive victory for the Union. The Confederate defeat at Five Forks weakened their hold on Petersburg and ultimately led to the fall of Richmond, the capital of the Confederacy.
Battle of Five Forks ends
Apr 1, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Five Forks ends on April 1, 1865. It was the final major battle of the American Civil War and resulted in a decisive victory for the Union army. The battle took place in Dinwiddie County, Virginia, and was fought between Union General Philip Sheridan and Confederate General George Pickett. Sheridan's forces successfully broke through the Confederate lines, forcing Pickett to withdraw. The Union victory at Five Forks played a crucial role in the eventual capture of Confederate capital Richmond and the surrender of General Robert E. Lee's army.
Image source: Battle of Five Forks

Battle of Petersburg ends
Apr 2, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Petersburg was a series of battles fought between the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by General Robert E. Lee, and the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by General Ulysses S. Grant. The battle took place from June 9, 1864, to April 2, 1865, during the American Civil War. The siege of Petersburg resulted in the eventual Union victory and the collapse of Confederate defenses. On April 2, 1865, the Confederate forces evacuated Petersburg, leading to the fall of Richmond and the end of the Civil War.
Battle of Appomattox Station
Apr 8, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Appomattox Station was fought on April 8, 1865, during the final days of the American Civil War. It was part of the Appomattox Campaign, which ultimately led to the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee and the end of the war. In this battle, Union forces under General George Custer clashed with Confederate forces under General Custis Lee. The Union forces were able to overpower the Confederates, leading to the capture of several Confederate soldiers and the destruction of a significant amount of Confederate supplies. This battle was one of the last engagements of the war and played a crucial role in the eventual surrender of the Confederacy.
Battle of Appomattox Station ends
Apr 8, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Appomattox Station ends on April 8, 1865. It was one of the final battles of the American Civil War. Confederate forces, led by General Robert E. Lee, were surrounded and outnumbered by Union forces. After a day of fierce fighting, the Confederates were forced to retreat. This defeat marked a significant turning point in the war, as it effectively ended Confederate resistance and led to the eventual surrender of General Lee's Army of Northern Virginia.
Image source: Battle of Appomattox Court House

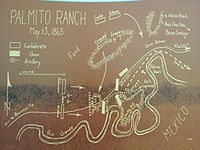
Battle of Palmito Ranch
May 12, 1865
% complete
The Battle of Palmito Ranch was fought on May 12-13, 1865, in Texas, near the present-day town of Brownsville. It was the final battle of the American Civil War, occurring more than a month after General Robert E. Lee's surrender at Appomattox Court House. The Confederate victory at Palmito Ranch was largely inconsequential in terms of its impact on the outcome of the war, but it marked the last engagement between Union and Confederate forces.
Image source: Battle of Palmito Ranch
Political and Legislative Developments
Emancipation Proclamation
Jan 1, 1863
% complete
The Emancipation Proclamation was issued by President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863. It declared that all slaves in Confederate territory were to be set free. However, it did not actually free any slaves in areas under Union control. The Proclamation was primarily a symbolic gesture to rally support for the Union cause and to encourage enslaved individuals to join the Union Army. It was a turning point in the war, shifting the focus towards the abolition of slavery.
Image source: Emancipation Proclamation

Emancipation Proclamation takes effect
Jan 1, 1863
% complete
The Emancipation Proclamation was an executive order issued by President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863. It declared that all slaves in Confederate-held territory were to be set free. However, it did not actually free any slaves immediately as it only applied to areas not under Union control. It was a significant turning point in the Civil War and laid the foundation for the eventual abolition of slavery.
Gettysburg Address
Nov 19, 1863
% complete
The Gettysburg Address is a speech that was delivered by President Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War. It was given on November 19, 1863, at the dedication ceremony of the Soldiers' National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. In the speech, Lincoln expressed the importance of preserving the Union and honoring the soldiers who had died in battle. The Gettysburg Address is considered one of the most famous speeches in American history and is often cited as a defining moment in the Civil War.
Image source: Gettysburg Address

Assassination of Abraham Lincoln
Apr 14, 1865
% complete
On April 14, 1865, Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth. Lincoln was attending a play at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C. when Booth entered the presidential box and shot him in the back of the head. Lincoln was carried to a nearby boarding house where he passed away the following day.
Image source: Assassination of Abraham Lincoln

Thirteenth Amendment Ratified
Dec 6, 1865
% complete
The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. It was ratified on December 6, 1865.
Image source: Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution

Surrender and Reconstruction
Surrender at Appomattox Court House
Apr 9, 1865
% complete
The Surrender at Appomattox Court House was the final surrender of the Confederate Army led by General Robert E. Lee to the Union Army led by General Ulysses S. Grant. It took place on April 9, 1865, in Appomattox County, Virginia, effectively ending the American Civil War.
Key Facts
- The Civil War began when Confederate forces attacked Fort Sumter in South Carolina.
- The Emancipation Proclamation, issued in 1863 by President Abraham Lincoln, declared the freedom of all slaves in Confederate territory.
- The Battle of Gettysburg, fought in 1863, was one of the bloodiest battles of the war and a turning point in favor of the Union.
- On April 9, 1865, Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House, effectively ending the war.
- The Civil War resulted in the abolition of slavery and a significant shift in the balance of power between the federal government and states.
Source
This Civil War in the United States timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].