-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Albert Einstein Timeline
(1879 - 1955)Early Life and Education
Birth of Albert Einstein
Mar 14, 1879
% complete
Albert Einstein is born in Ulm, Germany. He would go on to become one of the greatest physicists in history, revolutionizing our understanding of the universe with his theories.
Image source: Albert Einstein
Patent Office Job
Jun 23, 1902
% complete
Einstein begins working as a patent examiner at the Swiss Patent Office in Bern, Switzerland. This job provides him with a stable income and allows him to pursue his scientific interests in his spare time.
Image source: Einstein family

Theory of Relativity
Annus Mirabilis Papers
Jun 30, 1905
% complete
Einstein publishes four groundbreaking scientific papers, known as the Annus Mirabilis papers, which revolutionize the fields of physics and mathematics. These papers introduce the theory of relativity, the photoelectric effect, and the concept of mass-energy equivalence.
Special Theory of Relativity
Sep 26, 1905
% complete
Einstein publishes his paper on the special theory of relativity, introducing the famous equation E=mc² and challenging the classical understanding of space and time.
Image source: Special relativity

General Theory of Relativity
Nov 25, 1915
% complete
Einstein presents his general theory of relativity, providing a new understanding of gravity and proposing the existence of black holes and the bending of light around massive objects.
Image source: General relativity

Relativity's Confirmation by Eddington
May 29, 1919
% complete
Sir Arthur Eddington leads an expedition to Principe and Sobral to observe a total solar eclipse, confirming Einstein's theory of general relativity by observing the bending of starlight around the Sun.
Image source: Eddington experiment

Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen Paradox
May 15, 1935
% complete
Einstein, Boris Podolsky, and Nathan Rosen publish a paper introducing the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox, which challenges the completeness of quantum mechanics and raises questions about the nature of reality.
Image source: Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
Nobel Prize and Later Career
Einstein's Visit to the United States
Apr 2, 1921
% complete
Einstein visits the United States for the first time, delivering a series of lectures and sparking widespread interest in his scientific ideas.
Nobel Prize in Physics
Nov 9, 1922
% complete
Einstein is awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect, which laid the foundation for the development of quantum theory.
Image source: Nobel Prize in Physics

Theory of Brownian Motion
May 11, 1926
% complete
Einstein publishes his paper on the theory of Brownian motion, providing experimental evidence for the existence of atoms and molecules and confirming the atomic nature of matter.
Unified Field Theory
Dec 25, 1929
% complete
Einstein embarks on his quest for a unified field theory, attempting to unify the fundamental forces of nature into a single framework. Although he does not succeed in his lifetime, his work paves the way for future developments in theoretical physics.
Image source: Unified field theory

Emigration to the United States
Oct 17, 1933
% complete
Einstein leaves Germany due to the rise of Nazi power and moves to the United States, where he accepts a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey.
Image source: Hans Albert Einstein

Einstein's Unified Field Theory Lecture
Dec 20, 1933
% complete
Einstein delivers a lecture at the California Institute of Technology, presenting his latest attempts at formulating a unified field theory.
Einstein-Szilárd Letter
Aug 2, 1939
% complete
Einstein signs a letter to U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, warning him of the potential development of atomic weapons by Nazi Germany and urging the United States to initiate its own research.
Einstein's Letter to Roosevelt
Aug 2, 1939
% complete
Einstein signs a letter to U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, warning him of the potential development of atomic weapons by Nazi Germany and urging the United States to initiate its own research.
Manhattan Project
Aug 13, 1942
% complete
Einstein's theories indirectly contribute to the development of the atomic bomb through the Manhattan Project, a top-secret U.S. research program aimed at creating nuclear weapons during World War II.
Image source: Manhattan Project

Einstein's Letter to Roosevelt
Mar 25, 1945
% complete
Einstein writes a letter to President Roosevelt, urging him to consider the ethical implications of atomic weapons and advocating for international control of nuclear energy.
Image source: Einstein–Szilard letter

Formation of the State of Israel
May 14, 1948
% complete
Einstein is a prominent supporter of the Zionist movement and becomes involved in efforts to establish the State of Israel. He is offered the presidency of Israel but declines the offer.
Image source: History of Israel

Einstein's Letter to Chaim Weizmann
Nov 17, 1952
% complete
Einstein writes a letter to Chaim Weizmann, the first president of Israel, expressing his concerns about the potential dangers of nuclear weapons and advocating for peaceful uses of atomic energy.
Image source: Political views of Albert Einstein

Legacy and Impact
Death of Albert Einstein
Apr 18, 1955
% complete
Albert Einstein passes away at the age of 76 in Princeton, New Jersey, leaving behind a remarkable scientific legacy and a lasting impact on our understanding of the universe.
Einstein's Brain Autopsy
Apr 18, 1955
% complete
After Einstein's death, his brain is removed during the autopsy without the family's permission. It is later studied by scientists in an attempt to understand the neural basis of his genius.
Image source: Brain of Albert Einstein

Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity Celebrates 110 Years
Jun 30, 2015
% complete
The scientific community commemorates the 110th anniversary of Einstein's publication of the special theory of relativity, acknowledging its revolutionary ideas and lasting significance in the field of physics.
Einstein's Theory of Relativity Celebrates 100 Years
Nov 25, 2015
% complete
The scientific community celebrates the centennial of Einstein's theory of general relativity, recognizing its profound impact on our understanding of the universe and its continued relevance in modern physics.
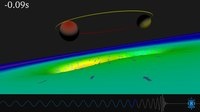
Einstein's Theory of Gravitational Waves Confirmed
Feb 11, 2016
% complete
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) announces the first direct detection of gravitational waves, confirming one of Einstein's predictions from his general theory of relativity.
Image source: Gravitational wave
Einstein's Manuscript Auction
Oct 24, 2017
% complete
A collection of Einstein's scientific manuscripts, including his groundbreaking papers, is auctioned in New York, highlighting the enduring fascination and value of his work.
Key Facts
- Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Germany.
- He developed the theory of relativity which revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity.
- In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect.
- Einstein was a pacifist and spoke out against war and the development of nuclear weapons.
- He died on April 18, 1955, in Princeton, New Jersey, United States.
Source
This Albert Einstein timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].